Often connections are TCP based, but sometimes UDP is all you have to test with, so I was quite surprised that testing that was quite forward. The solutions by [Wayback/Archive] How to Do a UDP Ping in Linux works on any platform where you can have nmap or netcat on installed (which by now is almost all platforms including Windows):
Archive for the ‘nmap’ Category
How to Do a UDP Ping in Linux
Posted by jpluimers on 2026/01/07
Posted in *nix, *nix-tools, Apple, BSD, Mac OS X / OS X / MacOS, netcat, nmap, Power User, Windows | Leave a Comment »
Windows chocolatey Wireshark install: ensure you install nmap too, so you have a pcap interface for capturing!
Posted by jpluimers on 2021/08/19
Wireshark is indispensable when doing network communications development or DevOps.
This is my choco-install-network-tools.bat batch file to install Wireshark and the pcap dependency which nmap provides:
choco install --yes nmap :: wireshark requires a pcap for capturing; nmap comes with npcap which fulfills this dependency :: see: :: - https://chocolatey.org/packages/wireshark :: - https://chocolatey.org/packages/win10pcap :: - https://chocolatey.org/packages/WinPcap :: - https://chocolatey.org/packages/nmap choco install --yes wireshark
Yes, I know: Windows Subsystem for Linux could have an easier installation, but the above:
- works on non-Windows-10 as well
- saves me from a Wireshark UI inside Windows Subsystem for Linux by fiddling with the X Window System (yes, it can be done: [WayBack] Hands-On with WSL: Running Graphical Apps — Virtualization Review)
See:
- [WayBack] Chocolatey Software | Wireshark 3.0.5
- [WayBack] Chocolatey Software | WinPcap 4.1.3.20161116 (development has stopped, plus it has a dependency on [WayBack] autohotkey.portable, which might interfere with [WayBack] autohotkey.install or [WayBack] autohotkey)
- [WayBack] Chocolatey Software | win10pcap (Install) 10.2.5002
- [WayBack] Chocolatey Software | Nmap 7.80
- [WayBack] Chocolatey Software | Npcap 0.86
–jeroen
Posted in *nix, *nix-tools, Communications Development, Development, Internet protocol suite, nmap, Power User, Software Development, Windows, Windows 10, Windows 8.1, WSL Windows Subsystem for Linux | Leave a Comment »
Obtaining system information from SMB – Nmap: Network Exploration and Security Auditing Cookbook – Second Edition
Posted by jpluimers on 2021/07/09
Based on
- [WayBack] Obtaining system information from SMB – Nmap: Network Exploration and Security Auditing Cookbook – Second Edition
- [WayBack] smb-os-discovery NSE Script
This scans the 192.168.1.0/24 network for SMB capable machines, and extracts information from them:
nmap -p139,445 --script smb-os-discovery 192.168.1.0/24
Note that experimenting this, I found out that nmap is also available on Chocolatey: [WayBack] Chocolatey Gallery | Nmap 7.70 (heck, since 2016, no less!).
I was hoping I wrote a little batch file around this, called find-smb-hosts.on.192.168.1.network.bat, because net view is working not so well on Windows 10 any more, but that failed, so here is the batch file:
@echo off :: only works from older versions than Windows 10 :: the delay is caused by the "net view" scanning the network :: the first for calls ping with the hostname :: the second for gets the IP and hostname without waiting for a ping result for /f "usebackq tokens=1* delims=\ " %%m in (`net view ^| findstr "\\"`) do ( for /f "usebackq tokens=2,3 delims=[] " %%h in (`ping -4 %%m -n 1 -w 1 ^| grep Pinging`) do ( echo %%i %%h ) ) goto :eof :: output of the first for without filtering (no starting newline): :: Server Name Remark :: :: ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- :: \\REVUE Samba 4.7.3-git.30.54c196e5d35SUSE-oS15.5-x86_64 :: \\VCS-CI :: The command completed successfully. :: output of the second for without filtering (including the starting newline): :: :: Pinging revue [192.168.1.62] with 32 bytes of data: :: Reply from 192.168.1.62: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=64 :: :: Ping statistics for 192.168.1.62: :: Packets: Sent = 1, Received = 1, Lost = 0 (0% loss), :: Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: :: Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
The above batch file delivered many more results than this line:
nmap -p139,445 --script smb-os-discovery 192.168.71.1/24 | grep -w "\(report\|Computer name\)"
–jeroen
Posted in *nix, *nix-tools, nmap, Power User | Leave a Comment »
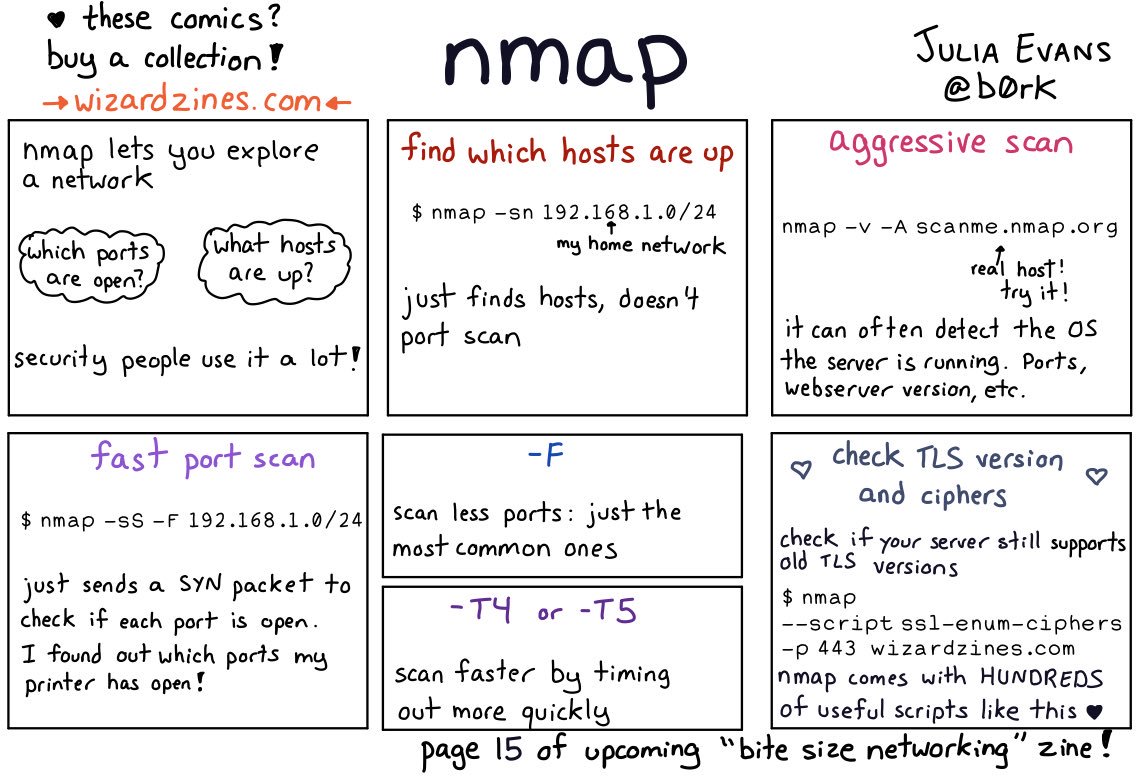
Thread by @b0rk: “nmap i haven’t used nmap much except to scan my home network for fun so if i missed something really important i’d love to know! […]”
Posted by jpluimers on 2021/02/05
[WayBack] Thread by @b0rk: “nmap i haven’t used nmap much except to scan my home network for fun so if i missed something really important i’d love to know! […]”
i haven’t used nmap much except to scan my home network for fun so if i missed something really important i’d love to know!also i need to find space in there somewhere for “if you don’t run nmap as root it can’t send icmp (ping) packets, it’s better to run nmap as root”
also be careful when nmapping in a network you don’t administer! it’s a popular hacking tool so using nmap is often discouraged / banned. i made all of the examples in this comic “
nmap scanme.nmap.org” and “nmap your home network” for a reason :)
There are are quite a few interesting comments on the thread:
- [WayBack] infosec pigeon on Twitter: “Just go nuts… nmap -Pn -sV –script vulners 10.0.0.0/24 -p-… “
- [WayBack] Josef Schugt on Twitter: “There also is a nice Android app for the same purpose that is GPL 3.0. It is called “Port Authority” https://f-droid.org/en/packages/com.aaronjwood.portauthority/ … – comes in handy to find the Raspberry Pis on the network using MAC address vendor identification 😍”
- [WayBack] Port Authority | F-Droid – Free and Open Source Android App Repository
- [WayBack] GitHub – aaronjwood/PortAuthority: A handy systems and security-focused tool, Port Authority is a very fast Android port scanner. Port Authority also allows you to quickly discover hosts on your network and will display useful network information about your device and other hosts.
- [WayBack] Port Authority – LAN Host Discovery & Port Scanner – Apps on Google Play
- [WayBack] jJ on Twitter: “Remote Root Exploit – Carrie-Anne Moss in “Matrix Reloaded” (2003) youtu.be/94F5S75ybSI via @YouTube… “
And it taught me about scanme.nmap.org: [WayBack] Go ahead and ScanMe!
Hello, and welcome to Scanme.Nmap.Org, a service provided by the Nmap Security Scanner Project and Insecure.Org.
We set up this machine to help folks learn about Nmap and also to test and make sure that their Nmap installation (or Internet connection) is working properly. You are authorized to scan this machine with Nmap or other port scanners. Try not to hammer on the server too hard. A few scans in a day is fine, but dont scan 100 times a day or use this site to test your ssh brute-force password cracking tool.
Thanks
–Fyodor
–jeroen
Posted in *nix, *nix-tools, nmap, Power User | Leave a Comment »
56 Linux Networking commands and scripts
Posted by jpluimers on 2021/01/25
Back in 2019, there were 56 commands and scripts covered. I wonder how many there are now.
An ongoing list of Linux Networking Commands and Scripts. These commands and scripts can be used to configure or troubleshoot your Linux network.
Source: [WayBack] 55 Linux Networking commands and scripts
List back then (which goes beyond just built-in commands: many commands from optional packages are here as well):
- arpwatch – Ethernet Activity Monitor.
- bmon – bandwidth monitor and rate estimator.
- bwm-ng – live network bandwidth monitor.
- curl – transferring data with URLs. (or try httpie)
- darkstat – captures network traffic, usage statistics.
- dhclient – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Client
- dig – query DNS servers for information.
- dstat – replacement for vmstat, iostat, mpstat, netstat and ifstat.
- ethtool – utility for controlling network drivers and hardware.
- gated – gateway routing daemon.
- host – DNS lookup utility.
- hping – TCP/IP packet assembler/analyzer.
- ibmonitor – shows bandwidth and total data transferred.
- ifstat – report network interfaces bandwidth.
- iftop – display bandwidth usage.
- ip (PDF file) – a command with more features that ifconfig (net-tools).
- iperf3 – network bandwidth measurement tool. (above screenshot Stacklinux VPS)
- iproute2 – collection of utilities for controlling TCP/IP.
- iptables – take control of network traffic.
- IPTraf – An IP Network Monitor.
- iputils – set of small useful utilities for Linux networking.
- jwhois (whois) – client for the whois service.
- “lsof -i” – reveal information about your network sockets.
- mtr – network diagnostic tool.
- net-tools – utilities include: arp, hostname, ifconfig, netstat, rarp, route, plipconfig, slattach, mii-tool, iptunnel and ipmaddr.
- ncat – improved re-implementation of the venerable netcat.
- netcat – networking utility for reading/writing network connections.
- nethogs – a small ‘net top’ tool.
- Netperf – Network bandwidth Testing.
- netsniff-ng – Swiss army knife for daily Linux network plumbing.
- netstat – Print network connections, routing tables, statistics, etc.
- netwatch – monitoring Network Connections.
- ngrep – grep applied to the network layer.
- nload – display network usage.
- nmap – network discovery and security auditing.
- nslookup – query Internet name servers interactively.
- ping – send icmp echo_request to network hosts.
- route – show / manipulate the IP routing table.
- slurm – network load monitor.
- snort – Network Intrusion Detection and Prevention System.
- smokeping – keeps track of your network latency.
- socat – establishes two bidirectional byte streams and transfers data between them.
- speedometer – Measure and display the rate of data across a network.
- speedtest-cli – test internet bandwidth using speedtest.net
- ss – utility to investigate sockets.
- ssh – secure system administration and file transfers over insecure networks.
- tcpdump – command-line packet analyzer.
- tcptrack – Displays information about tcp connections on a network interface.
- telnet – user interface to the TELNET protocol.
- tracepath – very similar function to traceroute.
- traceroute – print the route packets trace to network host.
- vnStat – network traffic monitor.
- wget – retrieving files using HTTP, HTTPS, FTP and FTPS.
- Wireless Tools for Linux – includes iwconfig, iwlist, iwspy, iwpriv and ifrename.
- Wireshark – network protocol analyzer.
Via:
- [WayBack] Trying to list All Linux Networking Commands and Scripts. Got to 55 and counting. #linux #commandline #networking – Hayden James – Google+
- [WayBack] Nice one – Jürgen Christoffel – Google+
–jeroen
Posted in *nix, *nix-tools, cURL, dig, Internet, nmap, Power User, SpeedTest, ssh/sshd, tcpdump, Wireshark | Leave a Comment »
Workaround for “Nmap 7.8 Assertion failed: htn.toclock_running == true” · Issue #1764 · nmap/nmap · GitHub
Posted by jpluimers on 2020/03/27
I got this on Windows 10, 8.1 and 7, MacOS and Linux:
C:\bin>nmap -sn 192.168.71.0/24
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2020-03-24 13:44 W. Europe Standard Time
Assertion failed: htn.toclock_running == true, file ..\Target.cc, line 503
Luckily [WayBack] Nmap 7.8 Assertion failed: htn.toclock_running == true · Issue #1764 · nmap/nmap · GitHub has a solution: add the --max-parallelism 100 parameter:
C:\bin>nmap -sn --max-parallelism 100 192.168.71.0/24
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2020-03-24 13:48 W. Europe Standard Time
Nmap scan report for 192.168.71.1
...
Host is up.
Nmap done: 256 IP addresses (50 hosts up) scanned in 54.07 seconds
The other workaround is to have at least one ARP request succeed.
Via [WayBack] “Assertion failed: htn.toclock_running == true, file ..\Target.cc, line 503” – Google Search
–jeroen
Posted in *nix, *nix-tools, nmap, Power User | Leave a Comment »
CitiZen nmap output
Posted by jpluimers on 2019/06/14
CitiZen nmap output: beagleboard with these open ports:
- 22 – ssh
- 80 – http
- 81 – unknown
- 1883 – mqtt
- 35505 – http
–jeroen
Posted in *nix, *nix-tools, nmap, Power User | Leave a Comment »
ScanSnap ix100 open ports
Posted by jpluimers on 2019/01/25
For my archive: the open ports on the ix100 WiFi connection:
# sudo nmap -O -v -A -p- -Pn 192.168.0.1
Password:
Starting Nmap 7.50 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2017-08-01 17:40 CEST
NSE: Loaded 144 scripts for scanning.
NSE: Script Pre-scanning.
Initiating NSE at 17:40
Completed NSE at 17:40, 0.00s elapsed
Initiating NSE at 17:40
Completed NSE at 17:40, 0.00s elapsed
Initiating ARP Ping Scan at 17:40
Scanning 192.168.0.1 [1 port]
Completed ARP Ping Scan at 17:40, 0.01s elapsed (1 total hosts)
Initiating Parallel DNS resolution of 1 host. at 17:40
Completed Parallel DNS resolution of 1 host. at 17:40, 0.03s elapsed
Initiating SYN Stealth Scan at 17:40
Scanning 192.168.0.1 [65535 ports]
Discovered open port 53218/tcp on 192.168.0.1
Discovered open port 53219/tcp on 192.168.0.1
Completed SYN Stealth Scan at 17:40, 51.05s elapsed (65535 total ports)
Initiating Service scan at 17:40
Scanning 2 services on 192.168.0.1
Service scan Timing: About 50.00% done; ETC: 17:41 (0:00:32 remaining)
Completed Service scan at 17:41, 31.85s elapsed (2 services on 1 host)
Initiating OS detection (try #1) against 192.168.0.1
NSE: Script scanning 192.168.0.1.
Initiating NSE at 17:41
Completed NSE at 17:41, 0.04s elapsed
Initiating NSE at 17:41
Completed NSE at 17:41, 0.02s elapsed
Nmap scan report for 192.168.0.1
Host is up (0.0037s latency).
Not shown: 65533 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
53218/tcp open unknown
| fingerprint-strings:
| DNSStatusRequest, DNSVersionBindReq, GenericLines, LPDString, NULL, WMSRequest, afp, oracle-tns:
|_ VENS
53219/tcp open unknown
| fingerprint-strings:
| DNSStatusRequest, DNSVersionBindReq, GenericLines, LPDString, NULL, WMSRequest, afp, oracle-tns:
|_ VENS
2 services unrecognized despite returning data. If you know the service/version, please submit the following fingerprints at https://nmap.org/cgi-bin/submit.cgi?new-service :
==============NEXT SERVICE FINGERPRINT (SUBMIT INDIVIDUALLY)==============
SF-Port53218-TCP:V=7.50%I=7%D=8/1%Time=5980A106%P=x86_64-apple-darwin16.6.
SF:0%r(NULL,10,"\0\0\0\x10VENS\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0")%r(GenericLines,10,"\0\0\0
SF:\x10VENS\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0")%r(DNSVersionBindReq,10,"\0\0\0\x10VENS\0\0\0
SF:\0\0\0\0\0")%r(DNSStatusRequest,10,"\0\0\0\x10VENS\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0")%r(
SF:LPDString,10,"\0\0\0\x10VENS\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0")%r(WMSRequest,10,"\0\0\0\
SF:x10VENS\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0")%r(oracle-tns,10,"\0\0\0\x10VENS\0\0\0\0\0\0\0
SF:\0")%r(afp,10,"\0\0\0\x10VENS\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0");
==============NEXT SERVICE FINGERPRINT (SUBMIT INDIVIDUALLY)==============
SF-Port53219-TCP:V=7.50%I=7%D=8/1%Time=5980A106%P=x86_64-apple-darwin16.6.
SF:0%r(NULL,10,"\0\0\0\x10VENS\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0")%r(GenericLines,10,"\0\0\0
SF:\x10VENS\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0")%r(DNSVersionBindReq,10,"\0\0\0\x10VENS\0\0\0
SF:\0\0\0\0\0")%r(DNSStatusRequest,10,"\0\0\0\x10VENS\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0")%r(
SF:LPDString,10,"\0\0\0\x10VENS\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0")%r(WMSRequest,10,"\0\0\0\
SF:x10VENS\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0")%r(oracle-tns,10,"\0\0\0\x10VENS\0\0\0\0\0\0\0
SF:\0")%r(afp,10,"\0\0\0\x10VENS\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0");
MAC Address: 84:25:3F:25:7F:21 (silex technology)
Device type: general purpose
Running: Linux 2.6.X
OS CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel:2.6
OS details: Linux 2.6.17 - 2.6.36
Uptime guess: 248.550 days (since Sat Nov 26 03:30:04 2016)
Network Distance: 1 hop
TCP Sequence Prediction: Difficulty=199 (Good luck!)
IP ID Sequence Generation: All zeros
TRACEROUTE
HOP RTT ADDRESS
1 3.66 ms 192.168.0.1
NSE: Script Post-scanning.
Initiating NSE at 17:41
Completed NSE at 17:41, 0.00s elapsed
Initiating NSE at 17:41
Completed NSE at 17:41, 0.00s elapsed
Read data files from: /usr/local/bin/../share/nmap
OS and Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 85.09 seconds
Raw packets sent: 65856 (2.898MB) | Rcvd: 65608 (2.625MB)
The nmap is aliased as nmap-fingerprint_host_all-ports-even-if-ping-fails
–jeroen
Posted in *nix, *nix-tools, Fujitsu ScanSnap, ix100, nmap, Power User, Scanners | Leave a Comment »
nmap for Windows: ncat as a TCP client to servers
Posted by jpluimers on 2018/11/16
Downloads are from a bit cryptic page [WayBack] Download the Free Nmap Security Scanner for Linux/Mac/Windows via [WayBack] Windows | Nmap Network Scanning.
An alternative is to go to [WayBack] nmap.org/dist, then search for the bottom most files having .exe or .zip extensions.
It is much more modern than netcat (see some links on that below) and has elaborate documentation:
- [WayBack] Ncat – Netcat for the 21st Century
- [WayBack] Ncat Users’ Guide
- [WayBack] Neat Tricks | Ncat Users’ Guide
Unwrap SSL
Suppose you need to connect to an IMAP server that requires SSL, but your mail reader doesn’t support SSL. Ncat can act as the encrypted bridge to connect the client and server. You will connect the mail client to a local port and Ncat will forward the traffic, encrypted, to the server. Here’s how to connect IMAP (port 143) on the local host to IMAP over SSL (port 993) on
imap.example.com.ncat -l localhost 143 –sh-exec “ncat –ssl imap.example.com 993”
- [WayBack] Neat Tricks | Ncat Users’ Guide
- [WayBack] Chapter 17. Ncat Reference Guide | Nmap Network Scanning
- [WayBack] Examples | Nmap Network ScanningCreate an HTTP proxy server on localhost port 8888.ncat -l –proxy-type http localhost 8888
As a comparison some netcat links:
- [WayBack] How To Use Netcat to Establish and Test TCP and UDP Connections on a VPS | DigitalOcean
- [WayBack] How to simulate a TCP/UDP client using Netcat – Ubidots Blog
- Netcat – Wikipedia
–jeroen
Posted in *nix, nmap, Power User | Leave a Comment »
Penetration Testing Tools and nmap Cheat Sheets
Posted by jpluimers on 2018/05/04
Via [WayBack] Penetration Testing Tools Cheat Sheet https://highon.coffee/blog/penetration-testing-tools-cheat-sheet/ #Security – This is why I Code – Google+
Penetration testing tools cheat sheet, a high level overview / quick reference cheat sheet for penetration testing.
Source: [Archive.is] Penetration Testing Tools Cheat Sheet
Nmap Cheat Sheet, examples and practical examples
Source: [Archive.is] Nmap Cheat Sheet
Posted in *nix, *nix-tools, nmap, Power User | Leave a Comment »