Every once in a while Jan Schaumann writes a long Twitter thread and saves it in a blog post. Always good ways to learn. This time it was no different: [Wayback/Archive] DNS Response Size started with
Archive for the ‘Wireshark’ Category
Guess the maximum DNS Response Size… (by Jan Schaumann)
Posted by jpluimers on 2023/12/26
Posted in Communications Development, Development, DNS, Internet, Internet protocol suite, IPv4, IPv6, Power User, TCP, tcpdump, UDP, Wireshark | Leave a Comment »
Wireshark Cheat Sheet – Commands, Captures, Filters, Shortcuts
Posted by jpluimers on 2023/02/28
[Wayback/Archive] Wireshark Cheat Sheet – Commands, Captures, Filters, Shortcuts
It is available both a huge [Wayback/Archive] jpg (2500×2096 pixels), so it already prints well on A5 or A4 sized paper for reference and as a [Wayback/Archive] PDF (so you can print it on even larger paper sizes).
Via: [Archive] Murdock (@Generic42) / Twitter in a DM.
–jeroen
Posted in *nix, *nix-tools, Communications Development, Development, Hardware, Network-and-equipment, Power User, Software Development, Wireshark | Leave a Comment »
console convert pcap to wav: not easily possible; use the WireShark GUI to do
Posted by jpluimers on 2021/12/01
Wanting a simple way on the console to convert a .pcap file to a .wav file, I searched for [Wayback] console convert pcap to wav – Google Search.
The reason is that [Wayback] fritzcap (written in Python) sometimes crashes while doing the conversion of a phone recording, so then only the .pcap file is available. I still want to figure this out, but given my health situation, I might not be able to in time.
Posted in *nix, *nix-tools, Audio, Development, ffmpeg, Fritz!, Fritz!Box, fritzcap, Hardware, Media, Network-and-equipment, Power User, Python, Scripting, Software Development, Wireshark | Leave a Comment »
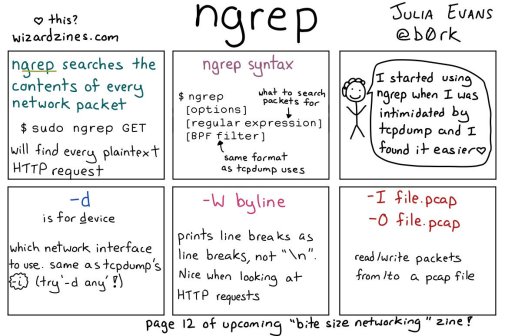
🔎Julia Evans🔍 on Twitter: “ngrep: grep your network!… “
Posted by jpluimers on 2021/02/16
[WayBack] 🔎Julia Evans🔍 on Twitter: “ngrep: grep your network!… “
So this taught me a new tool and other new things:
Posted in *nix, *nix-tools, Communications Development, Development, Internet protocol suite, Power User, Software Development, Wireshark | Leave a Comment »
56 Linux Networking commands and scripts
Posted by jpluimers on 2021/01/25
Back in 2019, there were 56 commands and scripts covered. I wonder how many there are now.
An ongoing list of Linux Networking Commands and Scripts. These commands and scripts can be used to configure or troubleshoot your Linux network.
Source: [WayBack] 55 Linux Networking commands and scripts
List back then (which goes beyond just built-in commands: many commands from optional packages are here as well):
- arpwatch – Ethernet Activity Monitor.
- bmon – bandwidth monitor and rate estimator.
- bwm-ng – live network bandwidth monitor.
- curl – transferring data with URLs. (or try httpie)
- darkstat – captures network traffic, usage statistics.
- dhclient – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Client
- dig – query DNS servers for information.
- dstat – replacement for vmstat, iostat, mpstat, netstat and ifstat.
- ethtool – utility for controlling network drivers and hardware.
- gated – gateway routing daemon.
- host – DNS lookup utility.
- hping – TCP/IP packet assembler/analyzer.
- ibmonitor – shows bandwidth and total data transferred.
- ifstat – report network interfaces bandwidth.
- iftop – display bandwidth usage.
- ip (PDF file) – a command with more features that ifconfig (net-tools).
- iperf3 – network bandwidth measurement tool. (above screenshot Stacklinux VPS)
- iproute2 – collection of utilities for controlling TCP/IP.
- iptables – take control of network traffic.
- IPTraf – An IP Network Monitor.
- iputils – set of small useful utilities for Linux networking.
- jwhois (whois) – client for the whois service.
- “lsof -i” – reveal information about your network sockets.
- mtr – network diagnostic tool.
- net-tools – utilities include: arp, hostname, ifconfig, netstat, rarp, route, plipconfig, slattach, mii-tool, iptunnel and ipmaddr.
- ncat – improved re-implementation of the venerable netcat.
- netcat – networking utility for reading/writing network connections.
- nethogs – a small ‘net top’ tool.
- Netperf – Network bandwidth Testing.
- netsniff-ng – Swiss army knife for daily Linux network plumbing.
- netstat – Print network connections, routing tables, statistics, etc.
- netwatch – monitoring Network Connections.
- ngrep – grep applied to the network layer.
- nload – display network usage.
- nmap – network discovery and security auditing.
- nslookup – query Internet name servers interactively.
- ping – send icmp echo_request to network hosts.
- route – show / manipulate the IP routing table.
- slurm – network load monitor.
- snort – Network Intrusion Detection and Prevention System.
- smokeping – keeps track of your network latency.
- socat – establishes two bidirectional byte streams and transfers data between them.
- speedometer – Measure and display the rate of data across a network.
- speedtest-cli – test internet bandwidth using speedtest.net
- ss – utility to investigate sockets.
- ssh – secure system administration and file transfers over insecure networks.
- tcpdump – command-line packet analyzer.
- tcptrack – Displays information about tcp connections on a network interface.
- telnet – user interface to the TELNET protocol.
- tracepath – very similar function to traceroute.
- traceroute – print the route packets trace to network host.
- vnStat – network traffic monitor.
- wget – retrieving files using HTTP, HTTPS, FTP and FTPS.
- Wireless Tools for Linux – includes iwconfig, iwlist, iwspy, iwpriv and ifrename.
- Wireshark – network protocol analyzer.
Via:
- [WayBack] Trying to list All Linux Networking Commands and Scripts. Got to 55 and counting. #linux #commandline #networking – Hayden James – Google+
- [WayBack] Nice one – Jürgen Christoffel – Google+
–jeroen
Posted in *nix, *nix-tools, cURL, dig, Internet, nmap, Power User, SpeedTest, ssh/sshd, tcpdump, Wireshark | Leave a Comment »