Q:
- “The volume can’t be ejected because it’s currently in use.“
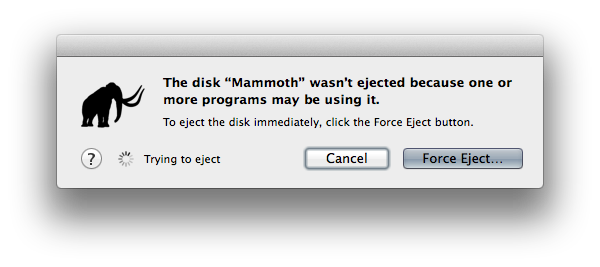
- “The disk “Diskname” wasn’t ejected because one or more programs may be using it.“.
- “
umount(/Volumes/Diskname): Resource busy -- try 'diskutil unmount'“
…
My question: How do I know what program is using my drive so I can properly quit that program and eject my drive?



A:
lsof is indeed your best bet. The fastest and easiest way would be this :-
sudo lsof /Volumes/myDrive
It can take a couple minutes to run, but once it’s complete, it gives you a list of open files on the disk. The output will look something like this:
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
mds 89 root 19r DIR 52,3 432 2 /Volumes/Photos
mds 89 root 23r DIR 52,3 432 2 /Volumes/Photos
Finder 681 alans 14r DIR 52,3 432 2 /Volumes/Photos
QuickLook 2158 alans 9r REG 52,3 1141591 78651 /Volumes/Photos/_tmp_iphone_10_backup/APC_1546.JPG
In this case, it’s the QuickLook application that has a file open. Closing the application directly is the best way to fix the issue. However, that’s not always possible. For example, QuickLook doesn’t show up as an application you can get to in the Dock.
If you can’t close the application manually, you can use the kill command to terminate it from the command line. To do that, use the PID from the second column as the ID to kill. From the above example, it would be:
kill 2158
Note that sometimes that doesn’t work and a more aggressive form of kill must be used. Here’s a series of escalating aggressiveness (using the example PID of 2158):
kill 2158
sudo kill 2158
sudo kill -INT 2158
sudo kill -KILL 2158
You should be able to eject the disk once the process/application has been killed.
One final note, lsof can take a minute or two. It can also hang, but you should give it at least a few minutes before you decide that’s what happened.
Also, sometimes the base command sudo lsof /Volumes/myDrive won’t find anything. If that happens, try adding the +D argument (i.e. sudo lsof +D /Volumes/myDrive). That will do a top down scan of the disk. It’ll take longer, but it should pick up anything that’s causing the disk to be un-ejectable.
(Hat tip to Alec Jacobson’s post for extra details.)
C:
sudo lsof /Volumes/drive is much faster than sudo lsof | grep /Volumes/drive













brew install --cask wireshark. If you use this, you may need to uninstall the non-cask version of wireshark prior to installing the cask.