One of the places explaining a more and more frequent error on Windows 7 installations is [Wayback/Archive.is] “You must provide a value expression on the right-hand side of the ‘-‘ operator.” · Issue #29 · shiftkey/chocolatey-beyondcompare:
Archive for the ‘Windows Server 2008’ Category
Chocolatey on Windows 7: “You must provide a value expression on the right-hand side of the ‘-‘ operator.”
Posted by jpluimers on 2022/06/08
Posted in Chocolatey, CommandLine, Development, Microsoft Surface on Windows 7, Power User, PowerShell, PowerShell, Scripting, Software Development, Windows, Windows 10, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2003 R2, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2 | Leave a Comment »
Windows: shutdown or reboot while preserving most of the running apps has been possible since…
Posted by jpluimers on 2022/05/26
Vista!
Shutting down or rebooting Windows allowing existing applications to reopen
Windows Vista introduced the /g switch in shutdown.exe and was unchanged in Windows 7:
/g Shutdown and restart the computer. After the system is rebooted, restart any registered applications.
I never noticed it until Windows 10 which began actively use it when applying system updates: then suddenly many of the previously running applications would reopen during startup.
Posted in Power User, Windows, Windows 10, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016, Windows Vista, Windows XP | Leave a Comment »
The Windows key has no Unicode equivalent, so use ⊞ like Wikipedia and many others do
Posted by jpluimers on 2021/08/23
lFor Mac keyboard keys, almost all (except the old solid and open Apple logo’s) have a Unicode code point, see for instance the modifier keys from the [WayBack] List of Mac/Apple keyboard symbols · GitHub (the “Alt” column has a solid Apple logo in the bottom right; on non-Mac systems it will look differently as it is in the Unicode private range: [WayBack] Unicode Character ” (U+F8FF): ‘<Private Use, Last>’):
Sym Key Alt ⌃ Control ⌥ Option ⇧ Shift ⌘ Command
These are the code points for the “Sym” column:
- ⌃ – [WayBack] Unicode Character ‘UP ARROWHEAD’ (U+2303) (less wide than the below three)
- ⌥ – [WayBack] Unicode Character ‘OPTION KEY’ (U+2325)
- ⇧ – [WayBack] Unicode Character ‘UPWARDS WHITE ARROW’ (U+21E7)
- ⌘ – [WayBack] Unicode Character ‘PLACE OF INTEREST SIGN’ (U+2318)
Keys on many platforms
Posted in Microsoft Surface on Windows 7, Power User, Windows, Windows 10, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows NT, Windows Server 2000, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2003 R2, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016, Windows Vista, Windows XP | 1 Comment »
How to turn on automatic logon in Windows
Posted by jpluimers on 2021/08/09
[WayBack] How to turn on automatic logon in Windows
Describes how to turn on the automatic logon feature in Windows by editing the registry.
Most archivals of the above post fail with a 404-error after briefly flashing the content, but this particular one usually succeeds displaying.
It is slightly different from the one referenced in my blog post automatic logon in Windows 2003, and because of the archival issues, I have quoted most of it below.
A few observations, at least in Windows 10 and 8.1:
- Major Windows 10 upgrades will disable the autologon: after each major upgrade, you have to re-apply the registry patches.
- If the user has a blank password, you can remove the DefaultPassword value.
- Empty passwords allow local logon (no network logon or remote desktop logon), no network access and no RunAs, which can actually help improve security. More on that in a later blog post
- For a local machine logon, you do not need the DefaultDomainName value either (despite many posts insisting you need them), but you can technically set it to the computer name using
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon" /v DefaultDomainName /t REG_SZ /d %ComputerName% /f - If another user logs on and off, the values keep preserved, so after a reboot, the correct user automatically logs on
- you need a full reboot cycle for this to take effect
- The AutoLogon tool does not allow blank passwords
I wrote a batch file enable-autologon-for-user-parameter.bat that makes it easier:
if [%1] == [] goto :help :enable reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon" /v AutoAdminLogon /t REG_SZ /d 1 /f :setUserName reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon" /v DefaultUserName /t REG_SZ /d %1 /f :removePasswordIfItExists reg delete "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon" /v DefaultPassword /f if [%2] == [] goto :eof :setPassword reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon" /v DefaultPassword /t REG_SZ /d %2 /f goto :eof :help echo Syntax: echo %0 username password
The article quote:
Posted in Batch-Files, Development, Microsoft Surface on Windows 7, Power User, Scripting, Software Development, Windows, Windows 10, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows 9, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2003 R2, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016, Windows Vista, Windows XP | Leave a Comment »
Error 0x8007232b or 0x8007007B occurs when you try to activate Windows
Posted by jpluimers on 2021/06/18
Since [WayBack/Archive.is] archival of Error 0x8007232b or 0x8007007B occurs when you try to activate Windows fails (the first indicates cookies need to be enabled, the second archives a page without support content), and the Google cached URL returns a 404, here is the full content:
Error 0x8007232b or 0x8007007B occurs when you try to activate Windows
Home users: This article is intended for use by support agents and IT professionals. If you’re looking for more information about Windows 10 activation error messages, see the following Windows website:
Symptoms
When you try to activate a Windows installation (client or server), you receive one or more error messages that resembles the following.
Error message 1
Activation Error: Code 0x8007232b
DNS Name does not existError message 2
Windows could not be activated.
Key management services (KMS) host could not be located in domain name system (DNS), please have your system administrator verify that a KMS is published correctly in DNS.Error: 0x8007232b
Description: DNS name does not exist.Error message 3
Error: 0x8007007B
The file name, directory name, or volume label syntax is incorrectResolution
To resolve this problem, use one or more of the following methods, as appropriate for your situation.
Method 1: Change the product key to an MAK
If KMS activation will not be used, and if there is no KMS server, the product key should be changed to an MAK. For Microsoft Developer Network (MSDN), or for TechNet, the stock-keeping units (SKUs) that are listed below the media are generally volume licensed-media, and the product key that’s provided is an MAK key.
To change the product key to an MAK, follow these steps:
- Open an elevated command prompt. To do this, use one of the following methods, as appropriate for your OS.
- At the command prompt, type the following command, and then press Enter:
slmgr -ipk xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxxNote The xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx placeholder represents your MAK product key.
Method 2: Configure a KMS host server for the clients to activate against
KMS activation requires that a KMS host server be configured for the clients to activate against. If there are no KMS host servers configured in your environment, install and activate one by using an appropriate KMS host server key. After you configure a computer on the network to host the KMS software, publish the Domain Name System (DNS) settings. For information about the KMS host server configuration process, see Set up a KMS host on a Windows Server 2008 R2 machine.
For more information about how to set up a KMS server and how to publish the DNS settings, go to the following Microsoft websites:
- Install a KMS host on a Windows Vista-based or Windows Server 2008-based computer
- Install KMS Hosts
- Deploy KMS Activation
- Volume activation in Windows Vista or Windows Server 2008, see the Volume Activation 2.0 Technical Guidance
- Planning for Volume Activation in Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2
Method 3: Manually create a KMS SRV record in a Microsoft DNS server
If your network has a KMS host computer set up, and if the client cannot locate a KMS host on the network for activation, follow these steps:
- Verify that the computer that has the KMS host installed and is activated by using a KMS key that’s registered in DNS. To do this, follow these steps:
- Open an elevated command prompt.Windows 7 or Windows Vista (Windows Server 2003)
Select Start > All Programs > Accessories, right-click Command Prompt, and then select Run as administrator. If you are prompted for an administrator password or for confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation.
Windows 8.1 and Windows 10 (Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2)
Press Windows logo key+X, and then select Command Prompt(Admin), or right-click the Start button, and then select Command Prompt(Admin). If you are prompted for an administrator password or for confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation.
- At the command prompt, type the following command, and then press Enter:
nslookup -type=all _vlmcs._tcp>kms.txt- Open the KMS.txt file that’s generated by the command. This file should contain one or more entries that resemble the following entry:
_vlmcs._tcp.contoso.com SRV service location: priority = 0 weight = 0 port = 1688 svr hostname = kms-server.contoso.com- If these “_vlmcs” entries are present, and if they contain the expected KMS host names, go to Method 4.
- Check the registry to determine whether the KMS host server is registering with DNS. By default, a KMS host server dynamically registers a DNS SRV record one time every 24 hours. To check this setting, follow these steps:
- Start Registry Editor.Windows 7 or Windows Vista
Click Start, type regedit, and then press Enter.
Windows 8.1 and Windows 10
Right-click Start, select Run, type regedit, and then press Enter.
- Locate and then click the following subkey:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\SLIf the DisableDnsPublishing subkey is present and has a value of 1, the KMS service does not register in DNS.
a If the DisableDnsPublishing subkey is missing, create a new DWORD value named DisableDnsPublishing. If dynamic registration is acceptable, change the subkey value to 0. To do this, right-click DisableDnsPublishing, click Modify, type 0 in the Value data box, and then click OK.
Note By default, this registry key has an undefined value that results in the dynamic registration every 24 hours.
If the DNS Server service does not support dynamic updates, or if dynamic updates are not occurring, the “VLMCS._TCP, SRV” record can be manually registered.
To manually create a KMS SRV record in a Microsoft DNS server, follow these steps:
- On the DNS server, open DNS Manager. To open DNS Manager, click Start, click Administrative Tools, and then click DNS.
- Click the DNS server where you have to create the SRV resource record.
- In the console tree, expand Forward Lookup Zones, right-click the domain, and then click Other New Records.
- Scroll down the list, click Service Location (SRV), and then click Create Record.
- Type the following information:
Service: _VLMCS
Protocol: _TCP
Port number: 1688
Host offering the service: <FQDN_of_KMS_Host>
- When you are finished, click OK, and then click Done.
To manually create SRV records in a BIND 9.x Compliant DNS server include the following information when you create the record.
Note If your organization uses a non-Microsoft DNS server, you can create the required SRV records as long as the DNS server is BIND 9.x compliant.
- Name=_vlmcs._TCP
- Type=SRV
- Priority = 0
- Weight = 0
- Port = 1688
- Hostname = <FQDN or A-Name of the KMS host>
Note The Priority and Weight fields are not used by KMS and are ignored by the KMS client. However, they must be included in the zone file.
To configure a BIND 9.x DNS server to support KMS auto-publishing, configure the BIND server to enable resource record updates from KMS hosts. For example, add the following line to the zone definition in Named.conf or in Named.conf.local:
allow-update { any; };Method 4: Manually assign a KMS server
By default, the KMS clients use the automatic discovery feature and query DNS for a list of servers that have published the _VLMCS record within the membership zone of the client. DNS returns the list of KMS hosts in a random order. The client picks a KMS host and tries to establish a session on it. If this attempt works, the client caches the server and tries to use it for the next renewal attempt. If the session setup fails, the client picks another server randomly. We highly recommend that you use the automatic discovery feature. However, you can manually assign a KMS server. To do this, open an elevated command prompt on the KMS client.
- Open an elevated command prompt.Windows 7 or Vista (Windows Server 2003)
Click Start, type cmd in the Start Search box, right-click cmd.exe in the results list, and then click Run as administrator. If you are prompted for an administrator password or for confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation.
Windows 10 and Windows 8.1 (Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012)
Press the Windows logo key+X, and then select Command Prompt(Admin), or right-click Start, and then select Command Prompt(Admin). If you are prompted for an administrator password or for confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation.
- Use the following commands at an elevated command prompt:
- To assign a KMS host by using the FQDN of the host, type the following command:
cscript \windows\system32\slmgr.vbs -skms <KMS_FQDN>:<port>- To assign a KMS host by using the version 4 IP address of the host, type the following command:
cscript \windows\system32\slmgr.vbs -skms <IPv4Address><:port>- To assign a KMS host by using the version 6 IP address of the host, type the following command:
cscript \windows\system32\slmgr.vbs -skms <IPv6Address><:port>- To assign a KMS host by using the NETBIOS name of the host, type the following command:
cscript \windows\system32\slmgr.vbs -skms <NetbiosName><:port>- To revert to automatic discovery on a KMS client, type the following command:
cscript \windows\system32\slmgr.vbs –ckmsMethod 5: Automatically publish KMS in multiple DNS domains
If the previous methods have not resolved this problem, the problem may be related to the ability of the client to resolve the DNS name of the KMS server or to connect to the KMS server. If this is the problem, follow these steps:
Note Unless otherwsie stated, do the following steps on a KMS client that has experienced the error that is mentioned in the “Symptoms” section:
- At a command prompt, type the following command, and then press Enter:
IPCONFIG /all- From the command results, note the assigned IP address, the DNS server address, and the default gateway address.
- Verify basic IP connectivity to the DNS server by using the ping command. To do this, run the following command.
ping <DNS_Server_IP_address>Note If this command does not ping the server, this problem must be resolved first.
For more information about how to troubleshoot TCP/IP issues if you cannot ping the DNS server, see the Microsoft TechNet topic Troubleshooting TCP/IP.
- Verify that the search list of the primary DNS suffix contains the DNS domain suffix that the KMS host registered.For the computers that have joined the domain, the DNS automatic discovery of KMS requires that the DNS zone contains the SRV resource record for the KMS host. This DNS zone is the DNS zone that corresponds to either the primary DNS suffix of the computer or to the domain of the Active Directory DNS.
For workgroup computers, the DNS automatic discovery of KMS requires that the DNS zone contains the SRV resource record for the KMS host. This DNS zone is the DNS zone that corresponds to either the primary DNS suffix of the computer or to the DNS domain name that is assigned by the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). This domain name is defined by the option that has the code value of 15 as defined in Request for Comments (RFC) 2132.
- Verify that the KMS host SRV records are registered in DNS. At an elevated command prompt, type the following command, and then press Enter:
nslookup -type=all _vlmcs._tcp>kms.txt- Open the Kms.txt file that was generated by this command. This file should contain one or more entries that resemble the following:
_vlmcs._tcp.contoso.com SRV service location: priority = 0 weight = 0 port = 1688 svr hostname = kms-server.contoso.comVerify the IP address, host name, and port of the KMS host.
Note If the nslookup command finds the KMS host, it does not mean that the DNS client can find the KMS host. If the nslookup command finds the KMS host, and if you still cannot activate the KMS host server, check the other settings, such as the primary DNS suffix and the search list of the DNS suffix.
The SRV records are registered in the DNS zone that corresponds to the KMS host domain membership. For example, assume that a KMS host joins the contoso.com domain. In this scenario, the KMS host registers its VLMCS._TCP SRV record under the contoso.com DNS zone. Therefore, the VLMCS._TCP.CONTOSO.COM record is created.
If the clients are configured to use a different DNS zone, automatically publish KMS in multiple DNS domains. To do this, follow these steps:
- Log on to a KMS host.
- Open an elevated command prompt.Windows 7 or Vista (Windows Server 2003)
Select Start, type cmd in the Start Search box, right-click cmd.exe in the results list, and then select Run as administrator. If you are prompted for an administrator password or for confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation.
Windows 8.1 and Windows 10 (Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2)
Press the Windows logo key+X, and then select Command Prompt(Admin), or right-click Start, and then select Command Prompt(Admin). If you are prompted for an administrator password or for confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation.
- At the command prompt, type regedit.exe, and then press Enter.
- Locate and then click the following registry subkey:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\SL
- In the navigation pane, select SL.
- Right-click a blank area in the details pane, point to New, and then select Multi-String Value.
- Type DnsDomainPublishList as the name for the new value, and then press Enter.
- Right-click the new DnsDomainPublishList value, and then select Modify.
- In the Edit Multi-String dialog box, type each DNS domain suffix that is published by KMS on a separate line, and then select OK.
- In the Edit Multi-String dialog box, type each DNS domain suffix that is published by KMS on a separate line, and then select OK.Note For Windows 7 and for Windows Server 2008 R2, the format for DnsDomainPublishListdiffers.
For more information, see the Volume Activation Technical Reference Guide.
- Restart the Software Licensing service by using the Service administrative tool. This operation creates the SRV records.
- Verify that the host name that is returned in the last step can be resolved by using a typical method on the KMS client. When the name is resolved, also verify that the IP address that is returned is accurate. If either of these verifications fails, investigate this DNS client resolver issue.
- To use the KMS automatic discovery feature, run the following command at an elevated command prompt to clear any previously cached KMS host names:
cscript C:\Windows\System32\slmgr.vbs –ckms- If you believe that you have an SRV record issue, you can troubleshoot it by using one of the commands that are documented in “Method 4” to statically specify a KMS host. The following commands can be used to determine whether this is a name resolution issue or an SRV record issue. If none of these commands resolves the problem, you may be encountering a blocked port or an inaccessible host (see the “More Information” section).Run the following commands:
cscript \windows\system32\slmgr.vbs -skms <KMS_FQDN>:<port> cscript \windows\system32\slmgr.vbs –atoIf these commands resolve the problem, this is an SRV record issue. To fix it, you must troubleshoot the SRV record.
If these commands do not resolve the problem, run the following commands:
cscript \windows\system32\slmgr.vbs -skms <IP Address>:<port> cscript \windows\system32\slmgr.vbs –atoIf these commands resolve the problem, this is most likely a name resolution issue.
The 1688 TCP port is used for the activation communication between the KMS client and the KMS host. If the communication seems to be blocked, check the firewall configurations or anything else that may block the 1688 TCP port.
More Information
This problem may occur if one or more of the following conditions are true:
- You use volume-licensed media with a Volume License generic product key to install one of the following operating systems:
- Windows Server 2012 R2
- Windows Server 2012
- Windows Server 2008 R2
- Windows Server 2008
- Windows 10
- Windows 8.1
- Windows 8
- Windows 7
- Windows Vista Enterprise
- Windows Vista Business
- The activation wizard cannot connect to a Key Management Service (KMS) host computer.
When you try to activate the system, the activation wizard uses DNS to locate a corresponding computer that’s running the KMS software. If the wizard queries DNS and does not find the DNS entry for the KMS host computer, the wizard reports an error. If you have a KMS host computer set up, the correct DNS entries are not seen by the client computer. If you do not have a KMS host computer set up, you must either set up a KMS host computer or switch to an MAK product key method to activate your volume license installation.
Microsoft Developer Network (MSDN) and Microsoft TechNet provide volume-licensed media for the following operating system stock-keeping units (SKUs):
- Windows Server 2012 R2
- Windows Server 2012
- Windows Server 2008 R2
- Windows Server 2008
- Windows 10 Enterprise
- Windows 8.1 Enterprise
- Windows 8 Enterprise
- Windows 7 Enterprise
- Windows Vista Enterprise
The volume-licensed media does not prompt you for a product key during installation. If you do not change the product key to the MSDN key, you receive an error message when you try to activate the operating system. If you use MSDN or TechNet media, you must change the product key to the MSDN product key. Use the “Method 1” procedure in the “Resolution” section to change the product key.
Note The MSDN or TechNet product key is the MAK product key.
References
For more information about Volume Activation, see the following Microsoft Knowledge Base article:
929712 Volume Activation information for Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7For more information about volume licensing, go to the Microsoft Volume Licensing website.
For more information about how to activate copies of Windows Vista or Windows Server 2008 that were installed by using volume-licensed media, go to the Product Activation and Key Informationwebpage.
–jeroen
Posted in Microsoft Surface on Windows 7, Power User, Windows, Windows 10, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016 | Leave a Comment »
Still relevant for current Windows versions: hard drive – defrag /x – consolidate free space not really working – Windows Server 2012 – Server Fault
Posted by jpluimers on 2021/06/11
From my answer at [WayBack] hard drive – defrag /x – consolidate free space not really working – Windows Server 2012 – Server Fault
I’ve tried many tools, starting with
defrag C: /X(which tries, but doesn’t give good results) and found out these steps give the best results:
- Perform an Ultradefrag full optimisation
- Perform a MyDefrag
Consolidate free spacescript on the drive.Note that MyDefrag (formerly named JkDefrag) is not maintained any more but the 4.3.1 version in the WayBack machine still works very well as the underlying defragmentation APIs in Windows haven’t changed.
References:
- (WayBack) UltraDefrag – An Open Source Defragmenter
- WayBack: MyDefrag v4.3.1
- (WayBack) MyDefrag – Wikipedia
- (WayBack) Defragmenting Files (Windows)
- (WayBack) The Challenge of Defragmenting an NTFS Partition | Systems Management content from Windows IT Pro
- (WayBack) windows – How do you defragment the MFT on an NTFS disk? – Super User
The original MyDefrag disappeared two times (temporarily in 2014 because the domain expired, then permanently in 2017 because the domain went off-line).
Luckily, the WayBack machine at archive.org has the latest version saved (not all the links from the archive.org search page have an executable as sometimes it shows the expired domain or a non-existing redirect when the domain got off-line):
- https://web.archive.org/web/20150811002116/http://www.mydefrag.com/Downloads/Download.php?File=MyDefrag-v4.3.1.exe
- https://web.archive.org/web/20120517021802/http://www.mydefrag.com/Downloads/Download.php?File=MyDefrag-v4.3.1.exe
- via [WayBack] map –unmap hanging on non-contiguous ISO file · Issue #212 · chenall/grub4dos · GitHub
- which also pointed to the installation documentation: [WayBack: MyDefrag v4.3.1]
Note that chocolatey install --yes mydefrag --version 4.3.11 fails because of the missing download. See [WayBack] Chocolatey Software | MyDefrag 4.3.1.
(The --version parameter trick is from [WayBack] Chocolatey – How to install hidden and unlisted package? – Super User, via [WayBack] “This package is unlisted and hidden from package listings.” – Google Search).
–jeroen
Posted in Power User, Windows, Windows 10, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016, Windows Vista, Windows XP | Leave a Comment »
How to install Telnet with only one command
Posted by jpluimers on 2020/12/01
Source: [WayBack] How to install Telnet with only one command:
dism /online /Enable-Feature /FeatureName:TelnetClient
–jeroen
Posted in Microsoft Surface on Windows 7, Power User, Windows, Windows 10, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows 9, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016, Windows Vista | Leave a Comment »
Using Chrome on Windows with a different proxy server than the system one (which is used by Internet Explorer)
Posted by jpluimers on 2019/10/25
By default, Chrome uses the same proxy server as Internet Explorer: the system one that your Chrome settings page accesses from chrome://settings/search#proxy through this command-line call:
"C:\Windows\system32\rundll32.exe" C:\Windows\system32\shell32.dll,Control_RunDLL C:\Windows\system32\inetcpl.cpl,,4
There is no GUI way inside Chrome to change this, but there is a command-line parameter: --proxy-server="ipaddress:port"
So create a new shortcut to Chrome, then you can change it.
This comes in very handy if you want to test
- some sessions through for instance Internet Explorer going through HTTP Fiddler (that defaults at localhost:8888)
- other sessions through Cntlm (that defaults to localhost:3128)
Some background information:
- [Archive.is] English@Life and Story: Configure the proxy server of google chrome independently.
- [WayBack] Google Chrome: How to Assign a Proxy Server that is Different from Internet Explorer’s Settings | a Tech-Recipes Tutorial.
- [WayBack] Chrome Web Store – Proxy Switchy!.
- [WayBack] Different Proxy Settings for IE and Chrome – Google Product Forums.
–jeroen
Posted in Chrome, Cntlm, NTLM, Power User, Web Browsers, Windows, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2003 R2, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Vista, Windows XP, Windows-Http-Proxy | Leave a Comment »
if statement – How to ask for batch file user input with a timeout – Stack Overflow
Posted by jpluimers on 2019/05/14
The trick is to use the choice command; see [WayBack] if statement – How to ask for batch file user input with a timeout – Stack Overflow
–jeroen
Posted in Batch-Files, Development, Microsoft Surface on Windows 7, Power User, Scripting, Software Development, Windows, Windows 10, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows 9, Windows Server 2000, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2003 R2, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016, Windows Vista, Windows XP | Leave a Comment »
Windows Server 2008 and Server 2008 R2 – OpenDNS
Posted by jpluimers on 2018/12/10
I did this a long time ago, but forgot to blog about it back then: [Archive.is] Windows Server 2008 and Server 2008 R2 – OpenDNS.
Summary:
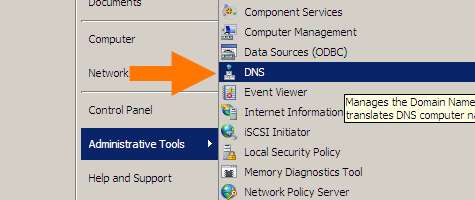
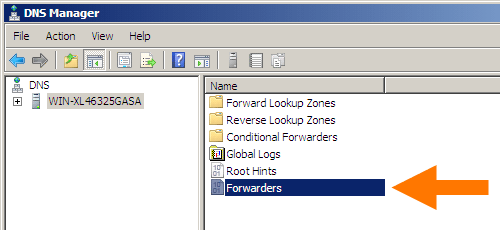
Start with the DNS manager:
%SystemRoot%\system32\dnsmgmt.msc /sThen open your machine, and double-click
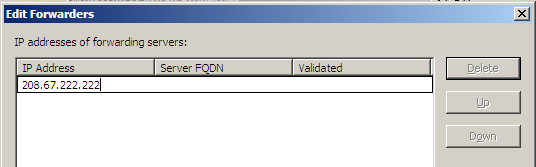
Forwarders:In the dialog, click the
Editbutton and add DNS servers (for instance Google DNS 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4).In my case it became this:
Google DNS servers added
Click
Donebuttons until all dialogs are closed.
–jeroen
Posted in DNS, Internet, Power User, Windows, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2 | Leave a Comment »